Featured Articles
- 01 What Is NTFS File System
- 02 What Is exFAT Format
- 03 What Is FAT File System Format (FAT, FAT16, FAT32)
- 04 What Is EXT2/3/4 File System (Linux) Format
- 05 NTFS VS exFAT VS FAT32, What's the Difference
- 06 How to Change File System to NTFS, FAT32, EXT
- 07 How to Convert File System - NTFS to FAT32
- 08 Best FAT32 Converter Free Download
- 09 Troubleshoot File System Errors
- 10 Fix File Is Too Large for Destination File System
- 11 Fix Volume Does Not Contain A Recognized File System
Overview
Which is better, exFAT or FAT32? exFAT is generally a better choice than FAT32 for larger storage devices and files due to its lack of file size limitations and its optimization for flash memory. FAT32, while highly compatible, has a 4GB file size limit and is best suited for smaller devices.
Quick Navigation:
- What is File System?
- The Differences Between exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS
- How to Convert Between exFAT and FAT32 and NTFS
When you plug a new USB flash drive or external hard drive in the Windows computer, the system will automatically open a window saying that your device needs to be formatted, and providing three different file formats: NTFS, FAT32, exFAT.
Many users know very little about these three file formats, they just operate according to the instructions of the pop-up window. Windows does not provide detailed explanations for the three formats, either. Don't worry, this article will explain these issues in detail.
What is File System?
First of all, we'd like to introduce what is the file system. The file system is the way the system stores and arranges files. The differences between different file systems are related to how data is stored on the hard drive. Also, they differ from each other in file names, file permissions, and other attributes.
The Windows operating system supports three different file systems: NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT. NTFS is the most widely used modern file system in recent years. Most of the built-in hard drives of Windows computers are in NTFS format. FAT32 has a longer history than NTFS. It cannot support some modern file format but is more compatible with different system platforms, such as Linux, Mac, and Android. exFAT is an alternative to the FAT32. Many devices and operating systems support this file system, but not many are currently used.
How to Format Write Protected USB/Pen Drive?
Here, you can find solutions to remove write protection from USB, pen drive, SD card, external hard drive, etc., and then format the device with ease.
The Differences Between exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS
Now it's time to illustrate the differences between these three file formats.
NTFS: NTFS stands for New Technology File System. It is the default new file system created for HDD and SSD by Microsoft and was popularized after Win 2000. NTFS performs quite well in security, ease of use, and stability. Now it is the most widely used file system and supports MBR hard drives up to 256TB, GPT hard drives up to 128EB. On the computer, it is suggested to choose NTFS when you partition the hard drive. But it is not recommended to use NTFS for the USB flash drive, as it will greatly shorten the lifespan.
- Pros: Supports large file sizes and partition sizes (up to 16EB theoretically), file permissions and encryption, journaling for better data integrity, compression, and other advanced features.
- Cons: Limited compatibility with non-Windows systems—macOS can only read (not write) NTFS by default, and some devices (like smart TVs or cameras) may not support it. Slightly more resource-intensive.
- Best for: Internal hard drives and SSDs used with Windows systems, especially when handling large files, requiring security features, or when performance and reliability are prioritized over broad compatibility.
FAT32: FAT32 stands for File Allocation Table 32. It was first introduced in Windows 95 to replace the old FAT16 file system. Generally, all USB flash drives have a FAT32 file system. The biggest advantage of FAT32 is its compatibility, it can be applied to any operating system. But the main drawback is that it only supports transferring a maximum single file size of 4GB. If you want to transfer files larger than 4GB, you would receive the error message "The file is too large for the destination file system".
- Pros: Highly compatible with various operating systems and devices, including older systems.
- Cons: Limited to 4GB file size and 8TB partition size.
- Best for: Smaller storage devices like USB drives and SD cards (especially those under 32GB) where compatibility is crucial and large files are not needed.
exFAT: exFAT stands for Extended File Allocation Table. It is a new file system created by Microsoft to replace the FAT32. The main difference between FAT32 and exFAT is that exFAT supports transferring files larger than 4GB. And it works well on both Windows and Mac computers, which is more compatible than NTFS. Its biggest disadvantage is that there is no file log function, so it can not record disk modification records.
- Pros: No file size limitations, making it suitable for large files and storage devices. It's designed for flash memory and is more modern than FAT32.
- Cons: Not as universally compatible as FAT32; some older devices or systems might not support it.
- Best for: Larger storage devices (like SD cards over 32GB, external hard drives) where large files need to be stored and used across different platforms.
How to Convert Between exFAT and FAT32 and NTFS for Free
As every file system has its defect, sometimes users may want to convert one file system to another. Is there any tool that can help users convert between file systems? Yes! One such tool recommended is EaseUS Partition Master Free.
As the name implies, EaseUS Partition Master Free is designed for users to manage partitions. It supports users to resize, move, merge, and create partitions. It also supports users to self-troubleshooting some simple problems, such as fix low disk space, check disk errors, and cannot extend volumes.
To convert between exFAT, FAT32, and NTFS, you just need simple clicks within EaseUS Partition Master Free. Now, please download this free tool, and follow our guide to see how to convert one file system to another. Here we will take converting FAT32 to NTFS as an example.
Part 1. Convert FAT32 to NTFS
Step 1. Install and launch EaseUS Partition Master on your computer.
Step 2. Go to the Disk Converter tab, select "FAT => NTFS" and click "Next."
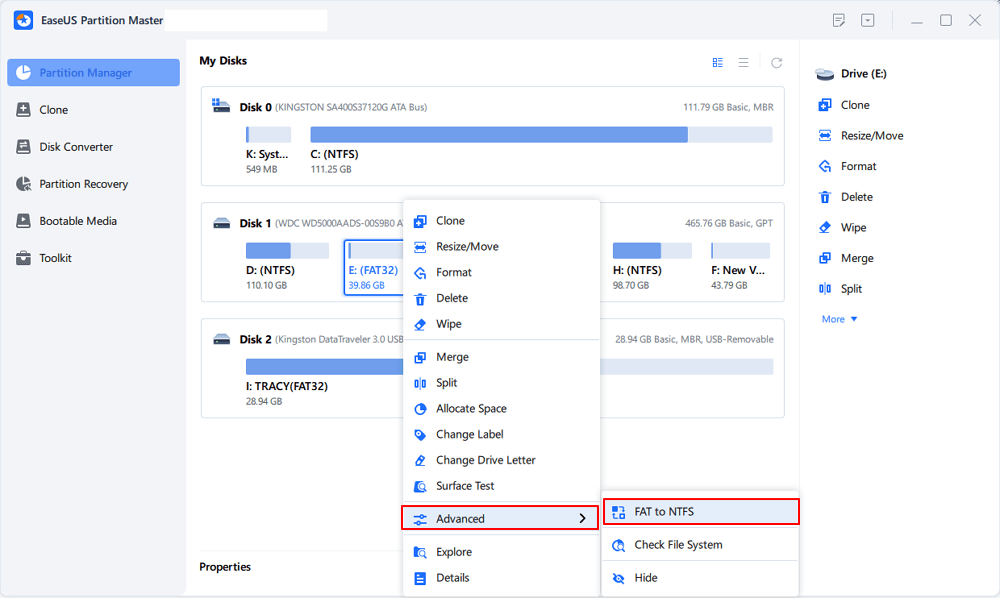
Step 3. Select the partition that you want to convert to NTFS and then click on "Convert." (Tick the "Show More" option in the panel's upper right corner to display the hidden partitions.)
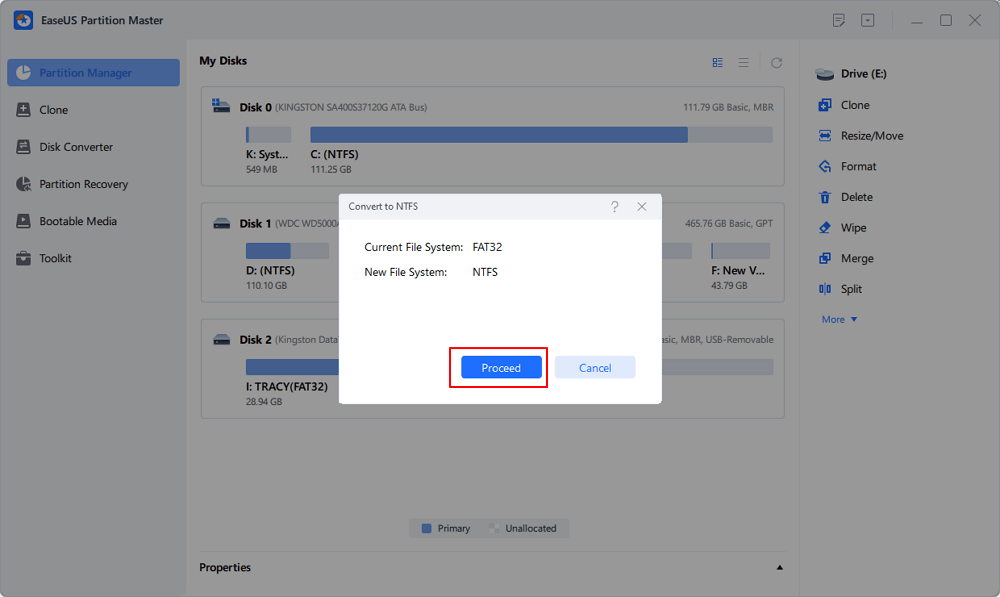
Step 4. Wait until the operation process is finished.
Part 2. Convert exFAT to FAT32
If you want to convert exFAT to FAT32, you can follow the guide below to format your device to FAT32.
Step 1. Launch EaseUS Partition Master, right-click the partition you intend to format and choose "Format".
Step 2. In the new window, enter the Partition label if you prefer to rename it, choose the FAT32/EXT2/EXT3/EXT4 file system, and set the cluster size according to your needs, then click "OK".
Step 3. Then you will see a warning window, click "Yes" in it to continue.
Step 4. Click the "Execute 1 Task(s)" button in the top-left corner to review the changes, then click "Apply" to start formatting the partition to FAT32/EXT2/EXT3/EXT4.
The Bottom Line
Some users might ask, which is better: exFAT, FAT32, or NTFS? Actually, there is no best choice. If you are formatting an HDD or SSD, then it is recommended to format it in NTFS. If you got a new USB flash drive, you'd better format it in FAT32 or exFAT. The main difference between FAT32 and exFAT is whether it can transfer files larger than 4GB. These three file systems have their advantages, flexible application of these file systems can help you better manage your partitions and drives.
FAQ About exFAT VS FAT32 VS NTFS
1. What's the main difference between exFAT, FAT32, NTFS?
FAT32, exFAT, and NTFS are different file systems used to organize and store data on storage devices. FAT32 is the oldest, offers good compatibility, but has limitations on file and partition sizes. exFAT is newer and designed for flash drives, offering better file size support than FAT32, but with potentially reduced compatibility compared to FAT32. NTFS is primarily used by Windows and offers advanced features like security permissions and journaling, but has limited compatibility with other operating systems.
2. Which format is better exFAT or NTFS?
It depends on your use case. NTFS is better suited for internal drives used with Windows, offering support for large files, permissions, encryption, and journaling. exFAT is better suited for external drives and USB sticks that need to work across different platforms, such as Windows, macOS, Linux, and some game consoles, especially when transferring large files.
3. Should I format FAT32 or exFAT?
Choose FAT32 only if you need maximum compatibility with very old devices or systems (like legacy cameras, routers, or older TVs). Otherwise, exFAT is the better choice for modern devices - it supports larger file sizes (over 4GB), has fewer limitations, and is widely supported across platforms.
Was This Page Helpful?
Sherly joined EaseUS in 2022 and she has always loved writing articles and enjoys the fun they bring. She receives professional training here, focusing on product performance and other relative knowledge. She has written over 200 articles to help people overcome computing issues.
Written by Tracy King
Tracy became a member of the EaseUS content team in 2013. Being a technical writer for over 10 years, she is enthusiastic about sharing tips to assist readers in resolving complex issues in disk management, file transfer, PC & Mac performance optimization, etc., like an expert.
Related Articles
-
How to Enable Secure Boot for Fortnite - Fixed
![author icon]() Sherly/Jan 29, 2026
Sherly/Jan 29, 2026 -
C Drive Is Raw Win 10: How to Repair - 5 Fixes
![author icon]() Sherly/Jan 29, 2026
Sherly/Jan 29, 2026 -
Failed to Open Device Getlasterror()=32: Fix Guiformat Error [100% Working Guide]
![author icon]() Cici/Jan 29, 2026
Cici/Jan 29, 2026 -
How to Recover Accidentally Deleted Operating System in Windows 11/10
![author icon]() Jean/Jan 29, 2026
Jean/Jan 29, 2026