Featured Articles
- 01 What Is NTFS File System
- 02 What Is exFAT Format
- 03 What Is FAT File System Format (FAT, FAT16, FAT32)
- 04 What Is EXT2/3/4 File System (Linux) Format
- 05 NTFS VS exFAT VS FAT32, What's the Difference
- 06 How to Change File System to NTFS, FAT32, EXT
- 07 How to Convert File System - NTFS to FAT32
- 08 Best FAT32 Converter Free Download
- 09 Troubleshoot File System Errors
- 10 Fix File Is Too Large for Destination File System
- 11 Fix Volume Does Not Contain A Recognized File System
In this article, you'll learn:
- What Is FAT File System?
- FAT (File Allocation Table) File System Structure
- Do I Need FAT File System?
- What Is the Difference Between FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32?
- What is the Difference between NTFS and FAT Files?
- How to Create FAT File System Partition?
FAT32 is one of the leading file systems in storage devices. So, what exactly is it?
File systems save the information and organize various types of data. The primary job of such systems is to create an index on physical storage to contain such data. One such file system is Fat32, which has been around since 1996.

So, what exactly is fat file system format? Moreover, what are the differences between Fat32 and other Fat file systems? To understand this, we have to dive in and understand how the file system works. SO, let's get started.
What Is FAT File System?
Fat file system, shortened from File Allocation Table, is a file system developed by Microsoft and Caldera development group for Windows computers. When Microsoft introduced Fat32 as a part of Windows 95 OSR2, it didn't take long to become one of the leading MBR/EBR file systems.
The file system uses a specific indexing system, which identifies streams of data and information stored on a physical device. At the time of formatting, the user can pick FAT as the primary file system. That's why it features a related list of passes for each specific data cluster.
While it's primarily a computer/PC partition, it has been used in various mobile phone devices in the past few years as the primary file system format. Also, since it's an 8-bit file system, the cluster numbers increase as the disk drive capacity goes up.
Therefore, the introduction of various file systems, such as:
- FAT12 - 12 bit
- FAT16 - 16 bit
- FAT32 - 32 bit
We should also clarify that the FAT file system has been used since 1977, but FAT32 was introduced in 1996.
FAT (File Allocation Table) File System Structure
The structure of FAT isn't difficult to understand. Considering it's an older technology, it uses comparatively simple sectors compared to today's leading file formats, such as NTFS. For instance, a FAT file system relies on various sectors, such as:
- Boot Sector: This is the part that contains the operating system's boot loader. Therefore, it's responsible for a computer device powering up and using the MRB or master boot record partition table. It's also known as the reserved sector.
- FAT Region: This part identifies the copies of the file on the File Allocation Table, which allows the system to allocate a specific cluster to each data stream.
- Data Region: This is where the data you use is stored, i.e., images, documents, audio files, or other media files. It's also generally the part that occupies the most clusters and the majority of a FAT partition.
- Root Directory Region: This sector is more of a directory table that specifies information regarding the files and their directory. This is found mainly in FAT16 and FAT12, as FAT32 stores root directories in the data region.
That's usually how the three main FAT file systems are structured, except for the minor difference of FAT32 from other bits.
Do I Need FAT File System?
FAT file systems are outdated, but that doesn't mean they are out of advantage. They are beneficial in many ways, particularly FAT32. For instance, compared to the earlier two FAT systems, i.e., FAT16 and FAT12, FAT32 has a lot more head space. Some advantages include:
- FAT32 was the first FAT file system to surpass the 1000GB mark, offering up to 2TB, while FAT16 only offers 2GB max.
- FAT32 doesn't waste any disk space storing system files, etc. That's why FAT32 formatted USBs and hard drives tend to have full storage, i.e., 500GB out of 500GB.
- FAT32 is supported by both Windows and Mac devices, making it easier to switch between them.
These are some primary reasons you might need a FAT file system. But, it's suggested that you don't go below FAT32.
What Is the Difference Between FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32?
There are a few key differences between the three primary FAT systems. First, the differences are allocated by their name and supported bits, such as:
- FAT32 is based on 32-bit
- FAT16 is based on 16-bit
- FAT12 is based on 12-bit
Another significant difference between them is their clusters, for instance:
- FAT32: This file system features 4 bytes per cluster or between 65526 and 268435456 clusters
- FAT16: This one features 2 bytes per cluster, or between 4087 and 65526 clusters
- FAT12: this features less than 4087 clusters
These are the primary differences between these three FAT file systems.
What is the Difference between NTFS and FAT Files?
NTFS and FAT are vastly different file systems. NTFS, or New Technology File System, was released in 1993, almost 16 years after the first FAT file system. But, to understand their differences, here are a few key ones:
| File Systems | Sharing Data | Activity Log | File compression | File Size | OS Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTFS | Doesn't support cross-platform, i.e., Mac to Windows and vice versa | Easily Restored | No compression supported | 4GB - 64GB | Only recognized operating systems |
| FAT | Supports cross-platform file sharing | No security and doesn't restore | No compression supported | 4GB Max | Supports more than one at a time |
Here's a visual graph of the FAT File System:
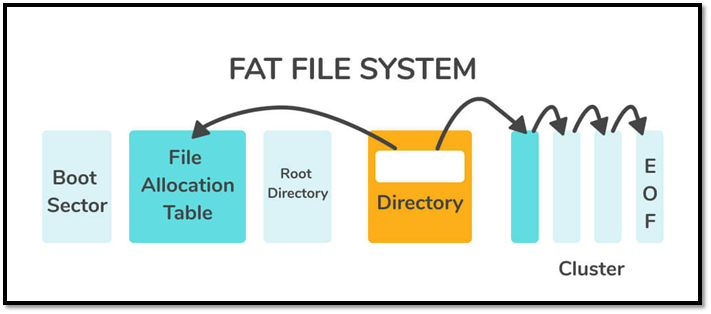
Here's one for NTFS:
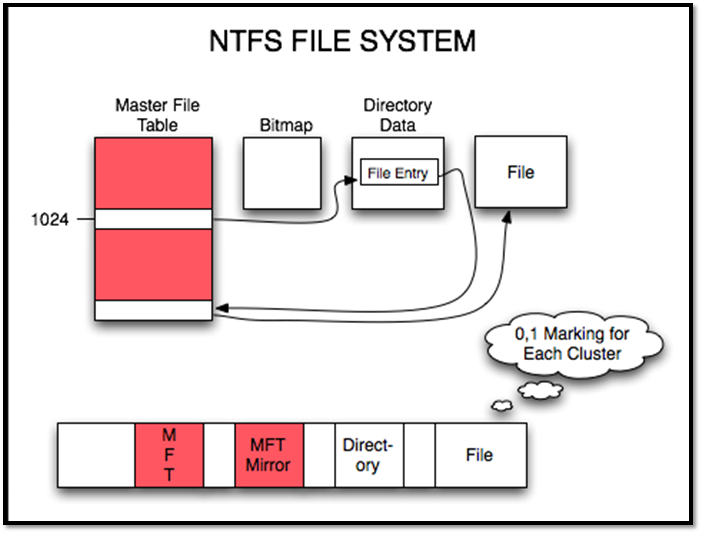
As you can see, both are pretty balanced. However, NTFS is much newer, so it's supported in many new storage and operating systems. But, a lot of users still employ FAT32 for cross-platform support.
How to Create FAT File System Partition?
There are plenty of ways you can create a FAT file system partition. Some of them include:
- Formatting from This PC or My Computer
- Formatting from Disk Management
- Picking Partition Type at the time of windows installation
- Formatting in Finder on a Mac
Format USB or External Hard Drive with EaseUS Partition Master
We talked about a few practical ways of creating FAT32 partitions. But, the most effective way is through a third-party program that allows you to access your partition through various operating systems.
One such program is EaseUS Partition Master. This outstanding partition tool allows you to format a USB or external Hard Drive for your PC.
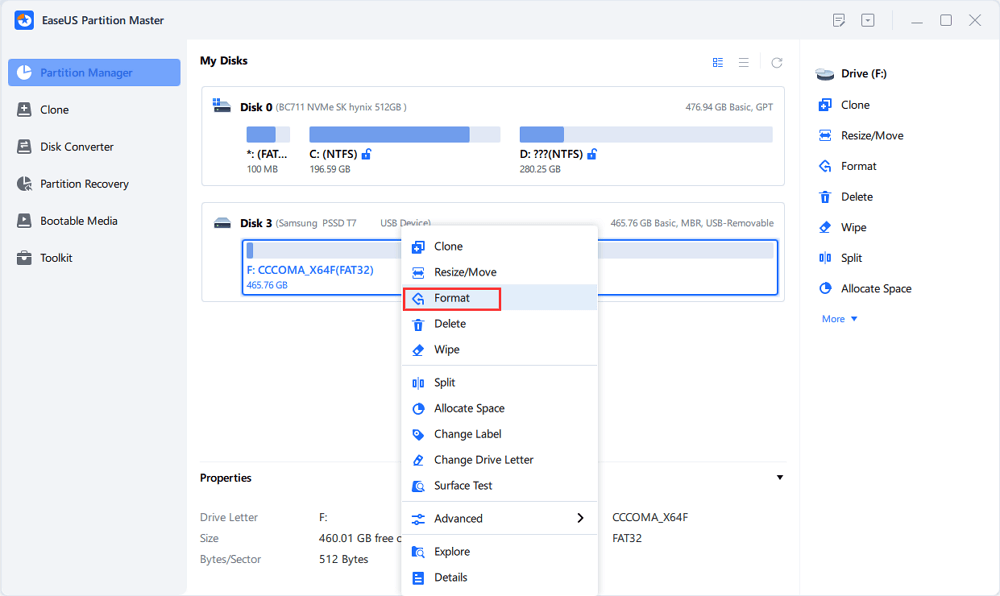
Step 1. Launch EaseUS Partition Master, right-click the partition on your external hard drive/USB/SD card which you want to format and choose the "Format" option.
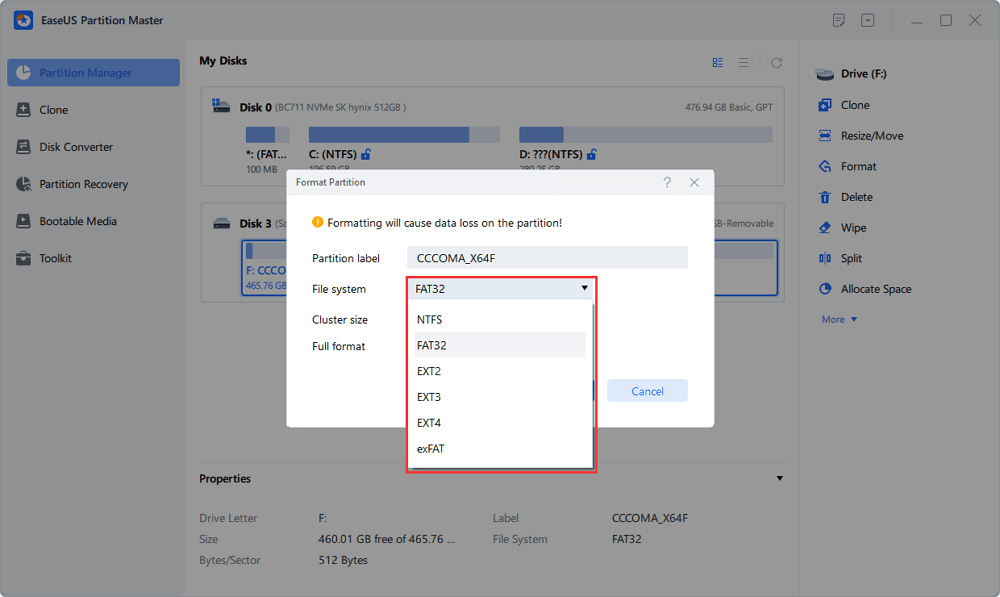
Step 2. Assign a new partition label, file system (NTFS/FAT32/EXT2/EXT3/EXT4/exFAT), and cluster size to the selected partition, then click "OK".
Step 3. In the Warning window, click "Yes" to continue.
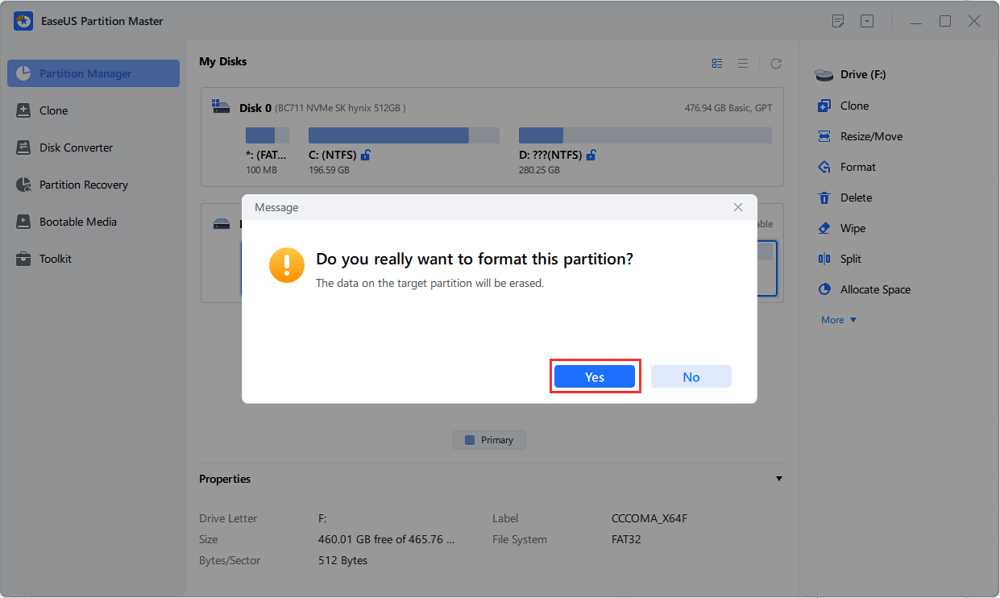
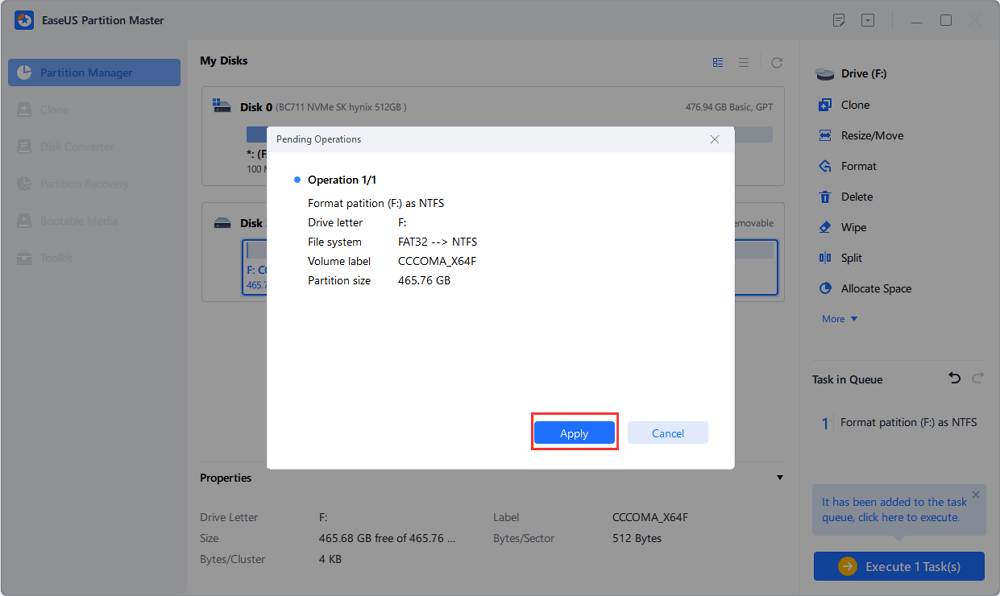
Step 4. Click the "Execute 1 Task(s)" button in the top-left corner to review the changes, then click "Apply" to start formatting your external hard drive/USB/SD card.
Why this tool out of all? Here are a few reasons:
- Merge two SSD drives into one
- Create, format, or delete partition without any hassle
- Effectively resize or remove partition without losing data
Besides that, you can also effectively change your partition's file system to FAT32.
Conclusion
We hope this article was helpful for your questions related to FAT and its related systems. While it's been around for more than four decades, it's still one of the most employed file systems and continues to give us reasons to use it.
Was This Page Helpful?
Sherly joined EaseUS in 2022 and she has always loved writing articles and enjoys the fun they bring. She receives professional training here, focusing on product performance and other relative knowledge. She has written over 200 articles to help people overcome computing issues.
Written by Tracy King
Tracy became a member of the EaseUS content team in 2013. Being a technical writer for over 10 years, she is enthusiastic about sharing tips to assist readers in resolving complex issues in disk management, file transfer, PC & Mac performance optimization, etc., like an expert.
Related Articles
-
CHKDSK /F /R/X Command to Fix Hard Drive Errors Win 10/11
![author icon]() Tracy King/Jan 29, 2026
Tracy King/Jan 29, 2026 -
Best Open Source Partition Software with Its Alternative Free Download
![author icon]() Tracy King/Jan 29, 2026
Tracy King/Jan 29, 2026 -
Basic Disk VS Dynamic Disk (The Features, Differences, and Conversion)
![author icon]() Brithny/Jan 29, 2026
Brithny/Jan 29, 2026 -
3 Simple Ways to Assign a Drive Letter in Windows 10/8/7
![author icon]() Cedric/Jan 29, 2026
Cedric/Jan 29, 2026