Featured Articles
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) recovery means recovering lost data from the corrupted or damaged RAID array. The RAID recovery process can be challenging, particularly in hardware failure or logical corruption cases. The professional RAID data recovery tool, such as EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, is designed to help users rebuild RAID and perform data recovery.
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drives to enhance performance and increase data redundancy by distributing data across the array. Depending on the specific RAID configuration used, it aims to provide fault tolerance, faster read/write operations, or larger storage capacities. RAID mainly employs RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10.
When the RAID is damaged, the volume becomes inaccessible, and the data is lost. You can't access or recover data from RAID hard drives directly. You need to reconstruct or rebuild the RAID configuration to get back lost data, which ordinary users find the most difficult. In this article, we provide professional RAID recovery software and services to help you restore lost data at any RAID level.
After showing you the way to recover data from RAID drives, we'll explain more about RAID and RAID failures. Now, move ro the RAID recovery part first and find a good RAID data recovery tool.
How to Recover Data from RAID Drives with RAID Recovery Software
Choosing professional RAID recovery software is greatly helpful for recovering data from RAID drives! EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard provides complete RAID data recovery solutions under Windows and Linux. Be it RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10, EaseUS RAID recovery software will help you recover data from any RAID hard drive, as long as your computer system can recognize it.
- Recover deleted, lost, or formatted data from RAID drives.
- Restore lost data from RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10.
- Recover data from enterprise RAIDs such as QNAP, Synology, WD, Buffalo, etc.
Don't hesitate to equip your computer with such a powerful tool. With this software, you can get files back from a RAID hard drive with the 3-step process: Scan disks > preview and select wanted files > recover data. Now, follow the steps below to recover RAID data with the help of EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard:
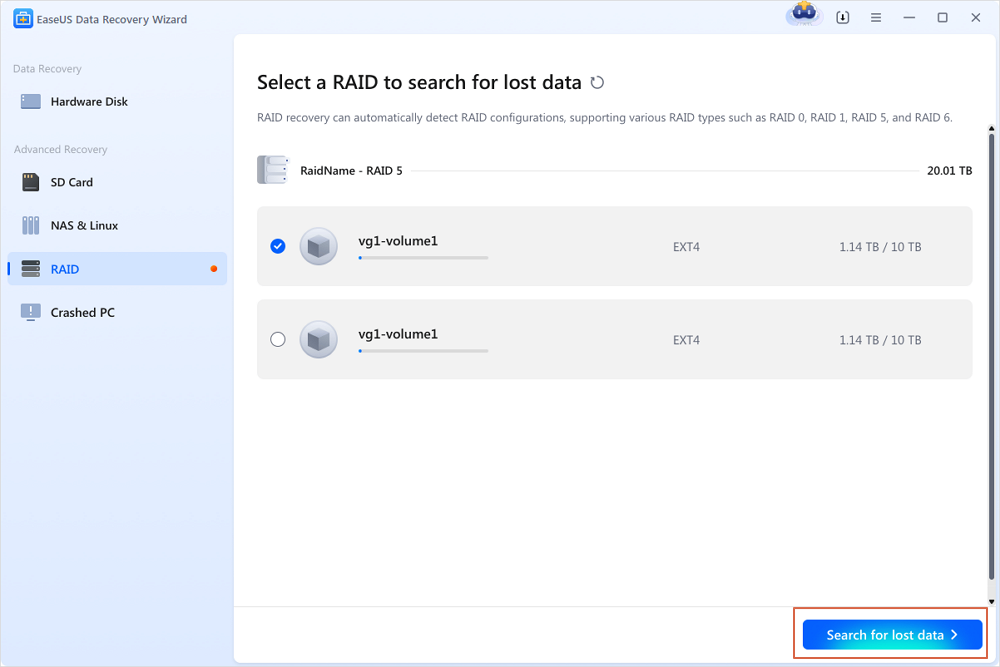
Step 1. Scan the RAID drive
Choose the RAID section from the sidebar, select the RAID 0/1/5/6 drive from which you wish to recover data, and then click "Search for lost data". Wait for the scanning process to finish, the deleted files will show up one by one.
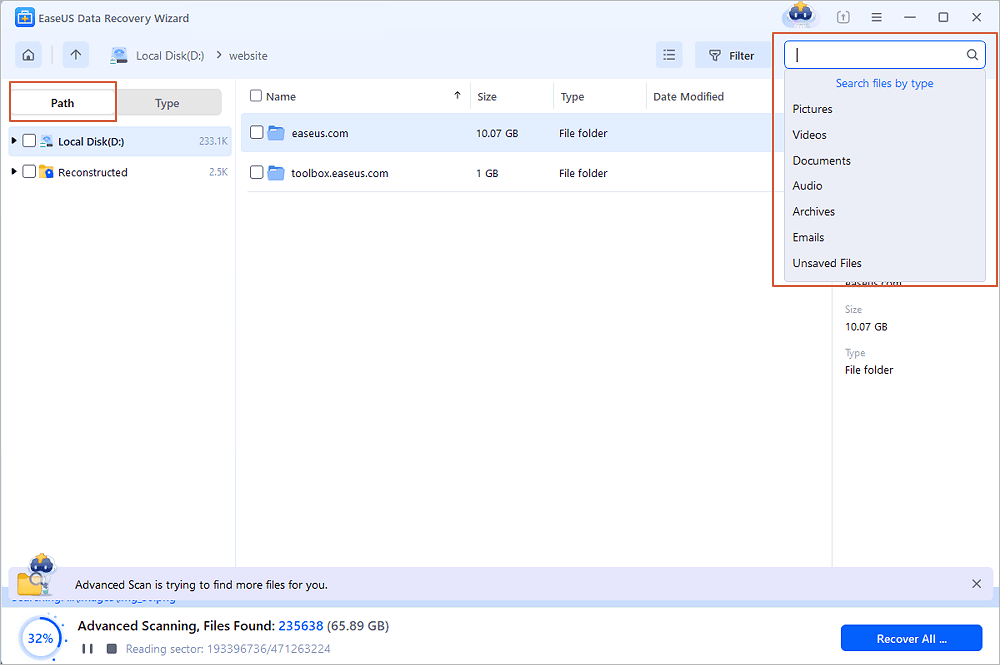
Step 2. Find and preview lost RAID files
You can use "Filter" as quick navigation to find deleted or lost files. Besides, you can also use Search to find your lost RAID drive files via its file name or file extension.
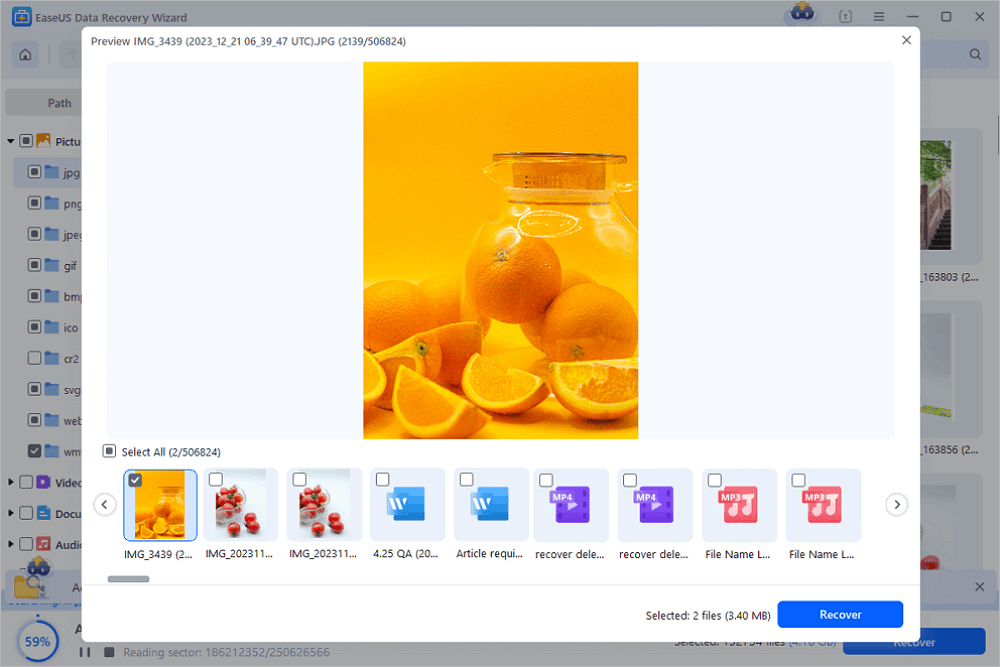
Step 3. Restore lost RAID drive files
Select the wanted files and click "Recover". Browse to save these files to another secure location.
💡Tip: You can restore data on the local disks, external hard drives, and also the cloud storage. Do not save them on the RAID drive again.
Also, watch this video tutorial to learn how to recover RAID data with EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard.
Feel free to share this RAID recovery guide on social media to help more readers fix RAID problem without losing data!
Perform RAID Recovery with RAID Data Recovery Services
RAID data recovery software can restore lost data well when the device has logical problems. However, if your RAID drive loses data in a very complex situation, you need to consult a data recovery service. EaseUS data recovery services offer advanced techniques and solutions to repair, recover, and reconstruct RAID data that has become inaccessible.
Our engineers have 20 years of experience in data recovery and disk repair. We can provide you with real-time remote recovery services; you do not need to mail your device, and we restore RAID data for you with minimal impact.
Consult with EaseUS data recovery experts for one-on-one manual recovery service. We could offer the following services after a FREE diagnosis. Our decades-experienced engineers are knowledgeable and can repair the damaged RAID structure and restore data from all RAID levels.
- Restore data from all RAID levels, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, etc.
- Recover data from enterprise RAIDs such as QNAP, Synology, WD, Buffalo, etc.
- Retrieve data from broken RAID in severe situations.
- Recover data from RAID remotely. No need to ship.
3 steps for RAID data recovery with our services:
✅Step 1. Request a free consultation: Contact our engineers for a free data recovery consultation. Our engineers will immediately check the condition of your device and evaluate the possibility of data recovery.
✅Step 2. Evaluation: Depending on the damage to your device and the difficulty of data recovery, we will conduct a quick and transparent assessment. Then, we will send you a written price quote.
✅Step 3. RAID Recovery: We will recover your data according to your chosen service level with our mutual agreement and your consent. You can track the data recovery process throughout.
RAID Failure Symptoms | 9 Symptoms
Different RAID levels and configurations have different fault manifestations. Early detection of these symptoms can help prevent or take action as soon as possible to reduce data loss. Here are some common RAID failure signs:
Error Messages: RAID disk drive problems, parity issues, controller failures, and data access faults will display different error codes or messages, which can help us diagnose the problem.
Inaccessible data or missing drives: File system or RAID configuration corruption will result in missing volumes or files or folders that are inaccessible.
System crashes or freezes: System hangs or crashes can indicate a RAID problem. This can be caused by disk errors, controller issues, or an ongoing but undetected rebuild process.
RAID rebuild failure: If RAID reconstruction fails repeatedly, stops midway, or takes a long time, it may indicate a problem with the drive or RAID controller.
Degraded RAID status: A RAID controller reporting a degraded status is also a sign of a RAID problem. This indicates that one or more disks have failed or are damaged and that the RAID's redundancy is compromised.
Slow performance: When the read/write speeds decline, you may likely encounter RAID failure.
Strange noises: If a RAID drive makes abnormal sounds when it is working, such as clicking, grinding, or beeping noises, it often signifies hardware failure. This is mostly related to head collisions, motor failures, or other machines in the drive.
Overheating: The increasing temperature of elevated operating might suggest a drive or system component is working harder than usual, potentially due to impending failure.
Unexpected and repeated restarts: If the system restarts unexpectedly or repeatedly during access, especially during I/O-intensive tasks, this signifies a RAID disk hardware problem.
If you encounter any of these symptoms, you must act promptly. Stop using your devices, check your RAID drives thoroughly, verify drive statuses, and apply RAID data recovery tools and services in complex scenarios to restore important files.
RAID Data Loss Common Causes
Users need a RAID recovery for the same reasons as they need a normal hard disk data recovery. A broken or corrupted RAID can result from human errors, hardware or software failure, malware infection, mechanical errors, power outages, bad sectors, abrupt system shutdown, etc.
File system corruption: The Ext4 and BRTFS are two core file systems of RAID drives. An internal error in the file system can cause data to become inaccessible, even if the RAID disk is not physically damaged.
Software failure: Software-related issues such as configuration errors, system problems, and driver compatibility issues may cause data loss. Misoperations can damage or change the RAID configuration. An operating system error or update problem may affect the normal running of the RAID array. Outdated or incompatible drivers and firmware may also cause RAID arrays to fail to work properly.
Hardware failure: Many hardware issues cause RAID data loss, including controller card failure, incorrect RAID physical component setups, head crashes, and firmware corruption.
Bad sectors: Over time, the hard disk may have bad sectors, and the data stored on the bad tracks may be damaged or lost.
Human errors: Deleting or overwriting files or volumes in a RAID array may result in significant data loss. Besides, RAID rebuilding and errors made during RAID arrays' installation, maintenance, or expansion may cause data loss.
Floods, fires, or other natural disasters: Physical disasters such as fire, flooding, or other object impact can cause devastating damage to the RAID array, rendering data inaccessible.
Electrical surges or power outages: Power supply interruption, Sudden power loss, or electrical surges can corrupt components within the RAID system, leading to data corruption or loss. The RAID system may encounter store fluctuations during read/write operations, which may damage data and cause the disk to become inaccessible.
Temperature and humidity: High temperatures can degrade the performance and lifespan of hard drives, eventually resulting in data loss. Moisture and contaminants can corrode connectors, circuit boards, or other hardware components, leading to intermittent or complete failure.
Virus or malware attacks: Viruses or malware may corrupt or even encrypt data stored in RAID arrays, resulting in data loss.
In all the above cases, stop all the operations. Preventive measures such as using high-quality hardware, maintaining proper cooling and ventilation, implementing a reliable power backup system, regularly monitoring RAID health, and having a robust disaster recovery plan are essential to minimize these risks. To maximize the chances of successful data retrieval, conduct RAID recovery software and specialized data recovery services with expertise in RAID systems.
Don't forget to share these common reasons that cause RAID data loss with your friends on social media!
RAID | Definition and RAID Levels
Before introducing the professional RAID data recovery software, let's learn some basic knowledge about RAID.
Definition of RAID
RAID, Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a data storage virtualization technology that provides a way of storing the same data in different places on multiple physical hard disks for the purpose of increasing your system performance or providing fault tolerance.
Different Levels of RAID
Data is allocated on RAID hard drives in different ways, referred to as RAID levels, including RAID 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 10. The explanations of commonest RAID levels:
| Level | Definition |
|---|---|
| RAID 0 | (Striped Disk Array without Fault Tolerance) RAID 0 provides data striping (spreading out blocks of each file across multiple disk drives) but no redundancy. This improves performance but does not deliver fault tolerance. If one drive fails then all data in the array is lost. |
| RAID 1 | (Mirroring Volume) RAID 1 provides disk mirroring. Level 1 provides twice the read transaction rate of single disks and the same write transaction rate as single disks. |
| RAID 5 | (Block Interleaved Distributed Parity) RAID 5 provides data striping at the byte level and also stripe error correction information. This results in excellent performance and good fault tolerance. Level 5 is one of the most popular implementations of the RAID. Give its popularity, it's necessary to know how to back up RAID drives to avoid complete data loss. |
| RAID 6 | (Independent data disks with double parity) RAID 6 requires a minimum of four disks. It uses two parity stripes on each disk and allows for two disk failures within the RAID set. The double parity makes it provide high fault tolerance and more expensive since the two extra disks required for parity. |
| RAID 10 | (A Mirror of Stripes) RAID 10, also called RAID 1+0, is not one of the original RAID levels, two RAID 0 stripes are created, and a RAID 1 mirror is created over them. Used for both replicating and sharing data among disks. |
Advantages of RAID
Generally, RAID uses multiple disks working together to increase overall system performance for computer users, especially server users. Besides, it also has the following benefits:
- Higher data security
- Higher fault tolerance
- Increased parity check and regularly check for any possible system crash
- Simultaneous reading and writing process
However, although RAID provides higher data security, data loss on RAID hard drives happens. You may suffer data loss on RAID disks or drives due to system crash, virus attack, power failure/surge, or other unexpected errors. You may think that RAID data recovery is complicated. As long as you get the right RAID recovery software, you can recover data from your RAID hard drives safely and effectively with ease.
RAID Data Recovery FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about RAID recovery:
1. What is the success rate of RAID data recovery?
The success rate of RAID data recovery is around 80% to 95%, depending on the type of RAID, extent of damage, and tools used. Success is higher when recovery is attempted promptly and no rebuilds were tried before.
2. How can I recover data from RAID 6?
It's recommended to apply professional RAID recovery software like EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard to extract data from RAID hard disks. If multiple disks failed or the array is misconfigured, consider professional RAID data recovery services.
3. Is it safe to apply free RAID recovery software?
It can be safe for diagnosis or testing, but free tools often lack full functionality or support for complex arrays. Always back up disk images first to avoid irreversible data loss during recovery attempts.
Was This Page Helpful?
Dany is an editor of EaseUS who lives and works in Chengdu, China. She focuses on writing articles about data recovery on Mac devices and PCs. She is devoted to improving her writing skills and enriching her professional knowledge. Dany also enjoys reading detective novels in her spare time.
Approved by Evan Galasso
Evan Galasso is a digital forensics and data recovery engineer with over 10 years of experience in the field. He presents opinions on the current state of storage media, reverse engineering of storage systems and firmware, and electro-mechanical systems of SSDs and HDDs.
Related Articles
-
2026 Formázatlan Ingyenes szoftver | Merevlemezek/USB meghajtók formázása könnyedén
![author icon]() Cedric/Feb 12, 2026
Cedric/Feb 12, 2026 -
NAND Recovery | Recover Lost Data from NAND Drive
![author icon]() Jaden/Jan 29, 2026
Jaden/Jan 29, 2026 -
How to Recover Data from Crashed Hard Drive Mac
![author icon]() Dany/Jan 19, 2026
Dany/Jan 19, 2026 -
Fix the Volume You Have Selected to Shrink May Be Corrupted [with Tips]
![author icon]() Jaden/Jan 19, 2026
Jaden/Jan 19, 2026

