Maintaining your hard drive's health is crucial to your computer's overall functioning. If your hard drive fails, you may lose vital data and experience severe downtime. That is why it is critical to check the health of your hard drive regularly to ensure that it is in good shape. One way to keep an eye on the hard disk's health is to use Windows's built-in command line tool, CMD or Command Prompt.
This guide will teach you how to check hard disk health using CMD. And you will also learn to use professional disk management tools to check bad sectors and disk health. By following the instructions in this post, you should be able to recognize any potential problems with the drive and take the appropriate steps before it's too late.
How to Check Hard Disk Health Using CMD
Command Prompt, simplified as CMD in Windows, is a command line interface similar to Terminal in Linux, allowing users to execute various commands via the shell. CHKDSK, which stands for Check Disk, is a crucial CMD command.
CMD provides the ability to check the health of your hard drive. However, it is not a comprehensive health check tool. I will highly recommend alternatives to CMD here - EaseUS Partition Master Free.
And analyze the advantages and disadvantages of both. You can choose the right method to check the health of your hard drive according to your needs.
| Comparison | EaseUS Partition Master | CMD |
|---|---|---|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
Since using the CMD alternative tool can solve the problem faster and can monitor more detailed hard drive health and SMART data, we will start with the CMD alternative tool to explain the detailed steps.
If you want to know more about repair tools on Windows 11, click the link below:
Top 8 Windows 11 Repair Tools | 2024 Best Picks
Are you looking for an excellent option to repair your Windows computer? Discover the top 8 solutions that can be used as a proper Windows 11 repair tool.
Check Hard Disk Health Using CMD Alternative
Now, let's explore an alternative way to CHKDSK on Windows. The Command Prompt is a little complex, and users may prefer a more intuitive, user-friendly method with a graphical user interface and additional built-in functions; this is where a third-party software, EaseUS Partition Master, fits in. It has more features than CMD, and it simplifies the process of the commands.
The EaseUS Partition Master is a reliable alternative to CMD's CHKDSK for evaluating the health of your hard drive. And it offers two ways to check hard disk:
Guide 1. Check Hard Disk Health
Guide 2. Check Hard Disk Bad Sector
You can run disk surface test to examine your hard disc's health and discover faulty sectors. And it is also easy to check hard drive health, including temperature and performance. Even if you are a novice, you can also master the tool. Let's look at the step-by-step guide.
Guide 1. Check Hard Disk Health
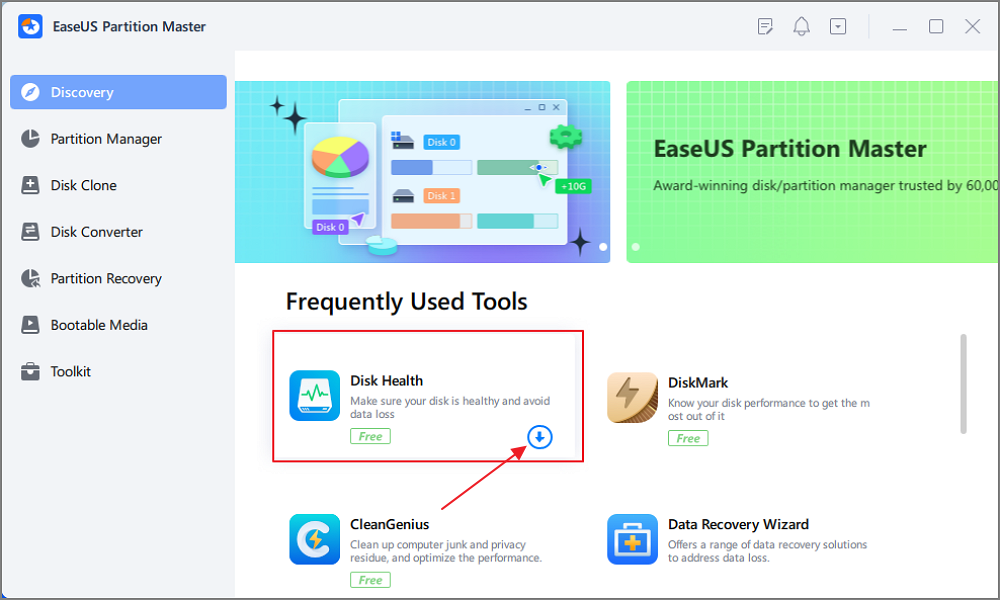
Step 1. Launch EaseUS Partition Master and click the blue arrow to activate the "Disk Health" feature under the "Discovery" section.
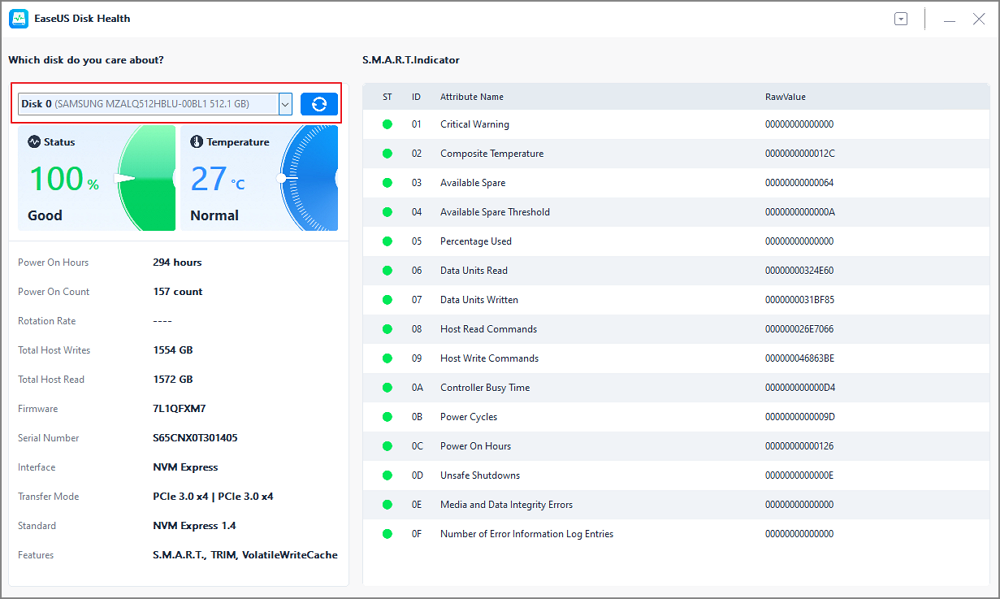
Step 2. Select the target disk and click the "Refresh" button. Then, you can see the health condition of your disk.
Guide 2. Check Hard Disk Bad Sector
Step 1. Open EaseUS Partition Master. Go to Toolkit and select "Bad Sector Scan."
Step 2. Tick "Scan Disk" and choose the target disk from the drop-down menu.
Step 3. Click "Scan" to apply the bad sector scaning process.
What Else Can EaseUS Partition Master Do?
EaseUS Partition Master is a great tool to check disk and partition errors and it has more features related to disk partition problems:
- Rebuild MBR
- Check hard drive health
- Check SD card health
- Repair bad sectors on external hard drive
- Resize partition on SSD or delete partition on SSD.
If you have any disk or partition problems, you can resort to EaseUS Partition Master, and you won't regret to download it!
Check Hard Disk Health Using CMD
In essence, CHKDSK, as the name implies, examines the disc for potential problems by scanning for flaws and recommending remedies. However, it requires you to be familiar with computer operations and does not provide you with a detailed SMART health report. For more comprehensive health check information, you can use a third-party tool - EaseUS Partition Master for hard drive health check.
Follow the steps below to use the CHKDSK command from the Command Line to assess the health of your hard disk on a computer running the Windows operating system.
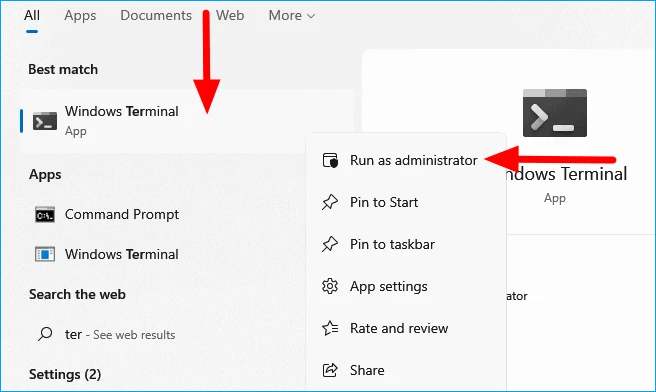
Step 1: Launch CMD, the Command Prompt, or the Windows Terminal with Administrative Privileges. Search for it in the Start Search Box. Right-click the main listed result and choose "Run as Administrator."
Step 2: Type in CHKDSK and press Enter. Windows will now examine your basic file system structure, name linkage, and security descriptors and let you know any possible problems.
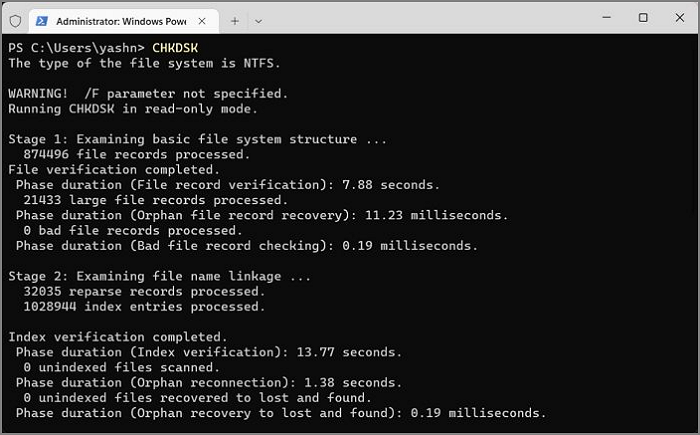
Step 3. You can also use CHKDSK inside CMD to fix errors on the disk. Instead of simply typing in CHKDSK, type in CHKDSK /f /r/x and press Enter.
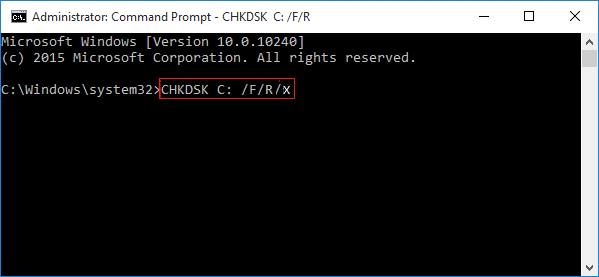
To know more about the CHKDSK command, click the button below to learn more details:
For new users unfamiliar with scripts or the Windows operating system, the Command Prompt and its shell can be overwhelming. If you prefer not to use the Command Prompt or want to check the health of your computer's hard drive with a different technique, move forward! And you can learn more details from this video.

Conclusion
Ultimately, it becomes highly critical to monitor the health of your hard disk regularly to have peace of mind regarding your data and confirm that it is performing on the right track. Command Prompt's CHKDSK is excellent for testing the health of your hard disk. Still, EaseUS Partition Master is a highly recommended alternative with a more user-friendly interface and additional functionality.
EaseUS Partition Master not only checks the health of your hard disk but also provides disk management capabilities such as partition resizing and disk cloning. EaseUS Partition Master is a dependable and convenient tool for running your hard disk smoothly.
FAQ of Check Hard Disk Health Using CMD
Let's look at some frequently asked questions concerning this process to get more information and troubleshooting tips.
1. How Do I Check My Hard Drive's Health?
You can download EaseUS's Partition Wizard or use the CHKDSK command with the Command Prompt. Here's how you can check your hard drive's health using the CHKDSK command.
Step 1. Right-click the Windows icon in the Taskbar and select Command Prompt (Admin) or Terminal (Admin).
Step 2. On the terminal, type CHKDSK and press Enter. Windows will now examine your computer's hard drives for faults and notify you of any that it finds.
2. How to check SSD health on CMD?
To check the health of your Solid State Drive (SSD), use the WIMC command, which is comparable to CHKDSK. WIMC, which stands for Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line, is a command-line interface for Windows.
Step 1. Open the Run Dialog, hit the Win + R keys on the keyboard, then type cmd, press Enter, or click the Run button.
Step 2. Now, in the command line, type wmic and press Enter. Then, type diskdrivegetsstatus, and press Enter.
If you see Status OK, the drive is in good working order. You might need to repair your disc drive if you detect anything else.
3. Can HDD health be repaired?
In limited instances, running CHKDSK with the "/f" flag may be capable of restoring the health of an HDD by scanning the drive for problems and attempting to correct them. However, if the damage to the HDD is extensive, it may not be repairable, and you will need to substitute the hard drive.
Was This Page Helpful?
Daisy is the Senior editor of the writing team for EaseUS. She has been working at EaseUS for over ten years, starting as a technical writer and moving on to being a team leader of the content group. As a professional author for over ten years, she writes a lot to help people overcome their tech troubles.
Cici is the junior editor of the writing team of EaseUS. She accepted the systematic training on computers at EaseUS for over one year. Now, she wrote a lot of professional articles to help people resolve the issues of hard drive corruption, computer boot errors, and disk partition problems.
Related Articles
-
How to Change Your IP Address on Computer
![author icon]() Daisy/2025-07-04
Daisy/2025-07-04 -
How to Fix Windows 11 Updates Are Underway Stuck | 8 Ways
![author icon]() Jerry/2025-07-10
Jerry/2025-07-10 -
⚠️Update Apple ID Settings Stuck on Your Mac? 6 Solutions to Fix It
![author icon]() Brithny/2025-07-04
Brithny/2025-07-04 -
[Step-by-step Guide] How to Reset Only C Drive in Windows 10 Safely
![author icon]() Jerry/2025-07-04
Jerry/2025-07-04
EaseUS Data Recovery Services
EaseUS data recovery experts have uneaqualed expertise to repair disks/systems and salvage data from all devices like RAID, HDD, SSD, USB, etc.