PAGE CONTENT:
What Is DAS? How Does It Work?
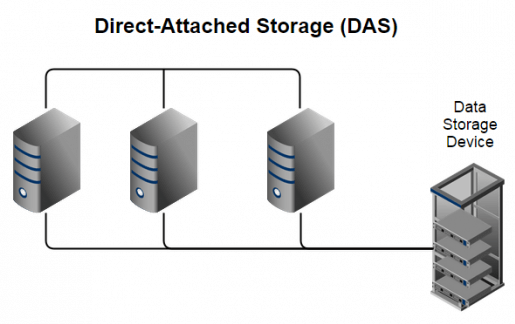
DAS, the abbreviation of Direct Attached Storage, is a kind of storage system that can be connected to computers, servers, or workstations without a network.
It is called direct attached storage because it doesn't connect to the network through Ethernet or Fibre Channel, nor use network devices such as hubs, switches, or routers to make storage available.
As the name suggests, it is directly connected to a computer or server. So, the data in it is only accessible to the device connected to it, and the device that controls it is not connected to the network. If a computer on the network wants to access the data in DAS, it must communicate with the computer to which DAS is attached.
Different Types of DAS
According to the device storage location, DAS can be divided into internal and external DAS, two types.
Internal DAS can be a storage device attached internally to a computer or server with a serial or parallel bus. One of the typical examples of internal DAS is an internal HDD in a computer. Actually, each computer is equipped with at least an internal DAS, like a traditional HDD, or a faster SSD connected with a SATA interface.
External DAS is placed outside the computer device, connecting to a server or workstation with USB, eSATA, SAS, or SCSI. Its typical examples are external hard drives or hard enclosures that allow connecting multiple devices.
According to different connecting devices, DAS has various forms, including SSD, hard drives, and optical devices like CDs, DVDs, and tape storage.
Pros & Cons of DAS
DAS has been widely used for its safe data protection because users don't need to access data without a network, significantly reducing the possibility of data leakage. Compared with NAS, DAS also takes advantage of lower cost and simplicity.
However, this does not mean that DAS is without drawbacks. Here we comprehensively list the advantages and disadvantages of DAS to help you better choose a data storage system.
Pros
- Provide better performance for users;
- Lower cost compared with NAS and SAN;
- Simple to use, IT professionals are not required, suitable for small business owners;
- Minimal maintenance cost.
Cons
- DAS has limited scalability;
- Lacks centralized management and backup capabilities;
- It can't be shared easily;
- If the driver fails, DAS isn't convenient to transfer;
- Difficult to upgrade.
Conclusion
So far, you must have known what DAS is, its working principles, and its pros and cons through the article. DAS plays an important role in expanding network connections. But it is not the only choice. NAS and SAN are also available for data connection which works with different data transfer modes. If you don't know which one suits you, refer to the differences between DAS vs. NAS, or NAS vs. SAN, it is a great way to help you make the right decision.
Was This Page Helpful?
Updated by Larissa
Larissa has rich experience in writing technical articles and is now a professional editor at EaseUS. She is good at writing articles about data recovery, disk cloning, disk partitioning, data backup, and other related knowledge. Her detailed and ultimate guides help users find effective solutions to their problems. She is fond of traveling, reading, and riding in her spare time.
Related Articles
-
What is a Client Server Network? How Does It Work?
 Daisy/2024-01-11
Daisy/2024-01-11 -
How to Use Device Encryption on Windows 11
 Jean/2024-07-01
Jean/2024-07-01 -
What Is Windows Update Assistant? [Everything You Need to Know]
 Jean/2024-02-21
Jean/2024-02-21 -
Discord Hardware Acceleration: Everything You Need to Know
 Daisy/2024-01-11
Daisy/2024-01-11
