When erasing sensitive data before disposing or repurposing a hard drive, users can utilize the zero-filling method. With the help of this solution, all the data on the drive is overwritten with zeros to make it impossible to recover any information previously stored on the drive. EaseUS Software will provide you with a step by step guide on it.
To carry out this disk management solution, you need to utilize the Command Prompt in Windows. While using CMD to zero-fill a hard drive, you will require a good understanding of command-line operations, which raises challenges for beginners. Therefore, users without technical skills should look for zero-fill hard drive CMD alternatives.
EaseUS Partition Master stands out as one such software that offers a more straightforward option to securely erase data without the need for complex commands. Throughout this article, we will familiarize you with the functionalities of this tool and teach you how to zero fill the hard drive using different methods.
Use the Safe Alternative to Command Prompt
As we have discussed, zero-filling a hard drive using CMD can prove to be a complex task for beginners. So, they need to use third-party software, such as EaseUS Partition Master Professional, to wipe all of their data from hard drives securely. Using this offline tool, you can completely format a hard drive or wipe out its partition to remove every single file of data before selling the computer.
Benefits of Using EaseUS Partition Master
- As an alternative to the "zero fill hard drive CMD" method, it provides a clearly guided interface to help beginners format their disks.
- This tool supports all the Windows versions, including Windows 11, 10, and XP, to help the vast user base benefit from its features.
- Other than wiping out your disks, this tool allows you to create, extend, or resize the disk partitions.
Here is how to use it:
We've set two options for you to wipe data. Choose the one you need.
Option 1. Wipe Partition
- Right-click the partition you want to erase data from, and choose "Wipe".
- In the new window, set the time for which you want to wipe your partition, then click "OK".
- Click the "Execute 1 Task(s)" button in the lower right corner, check the changes, then click "Apply".
Option 2. Wipe Disk
- Select the HDD/SSD. And right-click to choose "Wipe Disk".
- Set the number of times to wipe data. (You can set to 10 at most.) Then Click "OK".
- Click "Execute 1 Task(s)" and then click "Apply".
Besides that, this tool has the "Undo" functionality to prevent data loss in case you accidentally wipe out your hard drive. Moreover, users can even delete all the partitions from the external drives, SSDs, and USBs within a few clicks without writing any code. All in all, it emerges as the most secure and fastest solution for users who want to wipe out their hard drives completely.
How to Zero Fill Hard Drive via Command Prompt?
Users who have the technical knowledge to write and execute complex commands can utilize this method to wipe out partitions using CMD. Before carrying out the formatting process with this method, we recommend you back up your data for safety purposes in case you fail to execute the command correctly. Moreover, you must be careful while writing the commands and ensure you proofread them before hitting the "Enter" key.
Now, you are familiar with all the challenges you may face while zero-filling a hard drive using CMD. So, it is time to familiarize you with the detailed instructions on formatting your partitions with the help of the Command Prompt.
Step 1. To begin this zero-filling task, press the "Windows + R" keys simultaneously to open the "Run" dialog box. Afterward, enter "cmd" in the "Open" field and press the "Ctrl + Shift + Enter" combination to initiate the process of wiping out partitions.
Step 2. Once you enter this Command Prompt application, write a new command according to the "format X: /fs:NTFS /p:1" format.
- Here, X will represent the letter of the drive present in your hard disk.
- Moreover, NTFS is a file system you can identify within the "Properties" dialog box through the "This PC" folder.
- On the other hand, "p:1" shows that this process will write zeros to your hard drive only once. You can assign a bigger number to add zeros to the disk more times.
Step 3. Upon executing this command, a warning message will appear, after which you will need to enter the "y" command to confirm the operation. Moving forward, you have to wait a bit as this formatting task will take some time to complete.
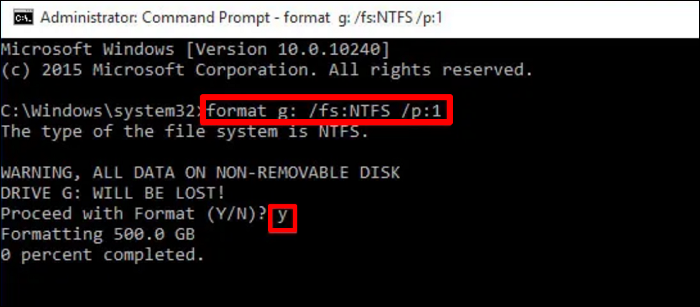
Step 4. After this process is completed, assign a name to your hard drive as a volume label. Alternatively, skip assigning the name and simply press "Enter" to process. Now, wait until the "Creating file system structures" appears on your screen and execute the "exit" command to complete this task.
Upon formatting your partitions using the "zero fill hard drive CMD" method, we recommend sharing this article in your circle to help others effectively manage their hard drive data.
Conclusion
You can write zero into a hard drive or wipe a disk using CMD. However, zero-filling a hard drive using CMD can prove to be difficult and time-consuming for most of users. Utilizing this method, you need to be very careful, as most beginners make mistakes while writing command lines. To avoid all such problems, users should go for third-party tools, such as EaseUS Partition Master.
With the help of this software, you get an optimized solution fit for beginners, as they can format hard drives within a few clicks. So, get your hands on this hard disk manager to wipe out every format individually and delete every single personal data file.
Zero Fill Hard Drive Using CMD FAQs
Once you read this article, you will become familiar with the two methods for zero-filling hard drives for data removal. Users who still have questions related to the functionalities of these methods can review the answers explained below.
1. What is a zero-fill hard disk?
When talking about data erasure methods, zero-filling a hard drive stands out as a technique to overwrite all data on a storage device by writing zeros (0s) across its entirety. Also known as the one-pass zeros erase method, it allows you to wipe out each partition or drive present within your hard disk. Moreover, this method is a secure way to erase data from various devices and drives permanently.
2. How to clear a hard drive using CMD?
To clean a hard drive using the Command Prompt, you can utilize the diskpart functionality using the below instructions.
- 1. First, users have to enter the Command Prompt application to execute the "diskpart" command to launch this feature for hard disk clearance.
- 2. Moving forward, type "list disk" and press the "Enter" key to reveal all the disks present within your system. Now, execute the "select disk n" command to pick the disk you want to clear with the help of the Command Prompt.
- 3. Finally, write and run the "Clean" command after selecting the disk to clear all the data within the hard disk.
3. When should users write zero on their hard disk?
You should consider writing zeros to your hard disk when you must securely erase all stored files. As this method effectively removes all traces of previous data, it proves to be valuable while selling, donating, or recycling your computer. Moreover, it ensures that sensitive information cannot be recovered with standard data recovery methods.
Was This Page Helpful?
Sherly joined EaseUS in 2022 and she has always loved writing articles and enjoys the fun they bring. She receives professional training here, focusing on product performance and other relative knowledge. She has written over 200 articles to help people overcome computing issues.
Related Articles
-
How to Fix Error Code 2003F When Entering Recovery Mode on macOS 13/12/11
![author icon]() Jaden/2025-01-24
Jaden/2025-01-24 -
Windows Solution: Can't Create Restore Point Windows 10
![author icon]() Daisy/2025-01-24
Daisy/2025-01-24 -
How to Disable Siri on Mac | for Beginners
![author icon]() Dany/2025-01-24
Dany/2025-01-24 -
How to Fix Macintosh HD Greyed Out in Disk Utility Without Data Loss [ 4 Solutions ]
![author icon]() Jaden/2025-01-24
Jaden/2025-01-24
EaseUS Data Recovery Services
EaseUS data recovery experts have uneaqualed expertise to repair disks/systems and salvage data from all devices like RAID, HDD, SSD, USB, etc.