Have you ever faced wifi connection issues in Windows? Have you ever met network slowdown issues after a Windows update? Are you trying to figure out what WINS is? Many people are curious about WINS after some suggestion pops up to check their WINS server when their router experiences excess traffic and name resolution slows down. Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) is a Microsoft Windows Service that effectively registers NetBIOS names of the computer on the local area network (LAN).
NetBIOS ( Network Basic Input/Output System) is a communication service that allows different computers to interact with each other across a LAN. WINS works after a name registration process is followed to register the NetBIOS name to IP address mapping on the WINS server. The WINS system consists of two parts: the WINS server and TCP/IP client software. The WINS server looks after the central Jet Database, replication, and client registration. The TCP/IP client software manages the querying of the name server.
You may face certain Wifi connection issues on your Windows due to a problem arising in NetBIOS name resolution in your router connection. WINS is the most viable solution to such problems in Routed networks that use NetBIOS.
What's The Difference Between WINS Server And DNS Server?
The difference between the WINS server and DNS server can be very minimal which may puzzle some users. But, they perform very different tasks. Thus, it is very important to know the difference between the two.
| WINS Server | DNS server |
|---|---|
| 1. WINS stands for Windows Internet Name Server. It is a Microsoft Windows Service that registers the NetBIOS name on the LAN. | 1. DNS stands for Domain Name System. It maps the domain names on the internet with IP addresses. |
| 2. NetBIOS in the old versions before Windows NT 4.0 only worked in NetBEUI protocol. WINS is a very vital part to resolve name resolution issues arising in the NetBEUI protocol. | 2. Microsoft made changes in NetBIOS to use TCP/IP stack instead of NetBEUI transport protocol. Thus, DNS servers can handle NetBIOS name requests now. Therefore, DNS has replaced WINS in the current Windows server. |
| 3. For example, if you type the command "Net use * \tree mainshare", it uses WINS to register the NetBIOS name "tree" to a LAN. Thus, WINS registers NetBIOS names to IP addresses. | 3. For example, if you type the command "Ping Tree.space.net'', it uses DNA to register Tree.space.net to an IP address. Thus, DNA registers TCP/IP host names to IP addresses. |
How To Find Your WINS Server?
Finding a WINS server can be a hectic task for someone who doesn't have the required knowledge to perform the complicated steps. So, you need to give your utmost attention while finding your WINS server.
First of all, you need to know your IP address in Windows to configure the WINS server. Follow these steps in order to find your IP address:
Step 1. Select "Start" > Settings > Network & sharing center, and then click on your wifi connection.
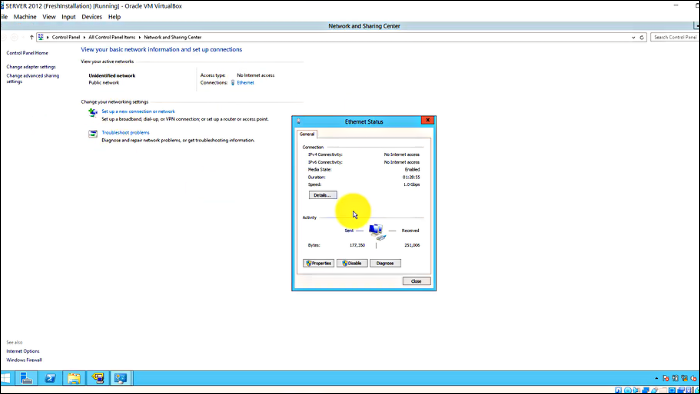
Step 2. Under Properties, click on Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4). Your IP address will be visible on the screen.after_clic
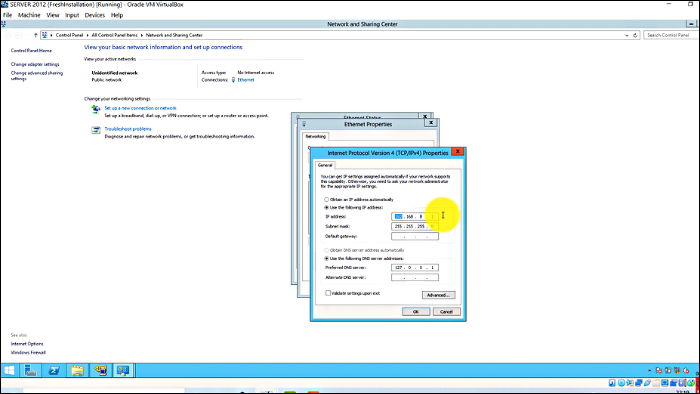
Now, to find your WINS server follow these steps:
Step 1: Select "Server Manager" > Add Roles and Feature Wizard > Features > WINS server
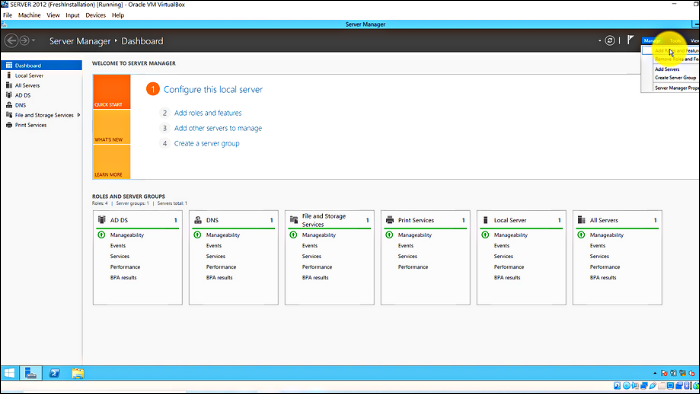
Step 2: Select "WINS server" > Add Features > Next > Install
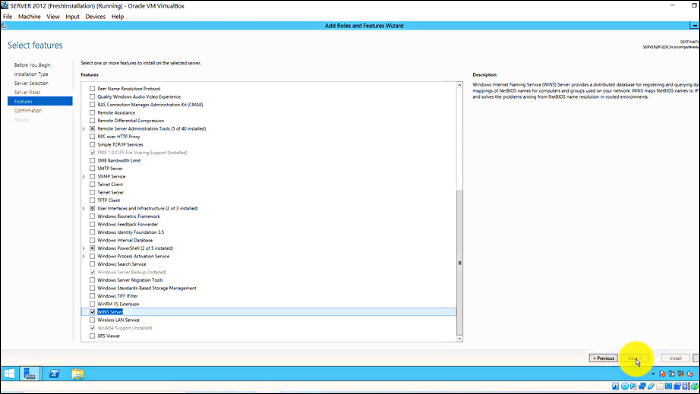
Step 3: After installing, follow the same process of finding your IP address and click advanced
Step 4: Select "WINS" > Add > Type your IP address > Add > Ok
Step 5: Then, select "Command Prompt" > Run as Administrator > Type the command "nbtstat -RR > Restart. WINS server will be activated on your Windows.
Do You Still Need A WINS Server?
WINS server has been there since the beginning of the Windows system. And all windows servers since Windows NT 4.0 have had WINS installed. This highlights the significance of the WINS server.
If you're using Windows NT 4.0 or other Windows servers launched before Windows NT 4.0, WINS is necessary. However, you can discontinue the WINS server in Windows server after Windows NT 4.0. All you need to do is decommission all the WINS servers in your network after identifying the servers using WINS replication.
However, it will be a large-scale incentive that will demand some strenuous work. Thus, the best option available is to keep the WINS server running on your Windows.
Final Words
WINS has been an essential part of Windows servers since the launch of the Windows system. You can always speed up name resolution on your network by having a WINS server. Moreover, WINS demands far less time and resources than other servers which is a noteworthy advantage. But, as time passed, the WINS server lost its significance to the DNA servers. However, it still holds its grounds and can be a vital part of your network if used properly.
Was This Page Helpful?
Daisy is the Senior editor of the writing team for EaseUS. She has been working at EaseUS for over ten years, starting as a technical writer and moving on to being a team leader of the content group. As a professional author for over ten years, she writes a lot to help people overcome their tech troubles.
Related Articles
-
OneDrive Backup vs. Sync: What Are the Differences
 Cedric/2024-01-11
Cedric/2024-01-11 -
What Is Vmmem Process and How to Fix Issues with Vmmem Process
 Daisy/2024-10-25
Daisy/2024-10-25 -
What Is RAW: the Comprehensive Definition and Meaning of RAW Conditions
 Jaden/2024-03-07
Jaden/2024-03-07 -
Rollback from Windows 11 to Windows 10 - 2 Methods
 Jean/2024-11-07
Jean/2024-11-07
