Being a technology user, you might be well aware of the importance of data and its access for the users, right?
Data loss is one of a technology user's most annoying conditions. Not everyone there can afford data losses. Keeping extreme consequences of data loss in mind, Microsoft offers a built-in protection feature in Windows - System Restore. It makes it easier for the users to return the last known stable condition of the OS. System Restore takes a snapshot of the PC's software, registry, and driver configuration at a specific point. Later, this snapshot makes it easier for it to revert the data.
This guide will introduce you to the System Restore Point in Windows and discuss its use.
What Is Restore Point in Windows
A System Restore point in Windows is an image of the PC's configuration and settings in the Windows registry that further helps it restore the system to an earlier date, especially when the system is working perfectly. It is a state of the computer that serves as a milestone from which you can revert the operating system's settings.
Restore Point creation happens in two scenarios—one when the Windows OS creates it and the second when the user chooses to create it.
Windows automatically creates the restore point whenever there is a significant event. It includes Windows Update, installation of a program, or when you make any changes to the critical system's settings.
As a user, you can also create a System Restore manually from the System Protection> System Properties Windows.
The System Restore point helps create a backup copy of the critical Windows operating system files and settings that further help recover the system to an earlier point. We would like to clarify that the system restore points affect theOS and the application files, not the user data. However, if your files are in critical places, which Windows adds to a System Restore point, it will also affect it.
How Does Restore Point in Windows Work
A restore point is an image of the state of the OS when anyone creates it. Anything on your System drive is part of the restore point, which includes configuration, settings, and registry of the Windows PC. Many users create it before a driver installation, a major Windows update, or anything critical to OS health.
The system restores points and helps users keep their PCs safe during bad Windows updates or system corruption issues. Moreover, the System restore point also saves existing applications & their data on your device.
Regarding the Corporate domain, the System Restore point doesn't save the Windows Security Account Manager and passwords that are not backed up. Once you have made a system restore option on your device, you will not be further able to get access to these files on your device.
In short, we can also say that the system restoring feature needs to be rejoined instantly to the domain when the corporate domain joined the computer loses its association.
Lastly, the system restores points and doesn't affect user data or files. It is not a complete backup but ensures users have safe access anytime. It doesn't delete personal files from your computer system and does not affect a system restore. One needs to be a bit careful as it usually fails to restore the files that are deleted accidentally.
You may be interested in How to Create System Restore Point Windows 10/11.
How to Recover with a Restore Point in Windows
Recovering with a restore point in Windows is a straightforward process that hardly requires a few clicks to make. If you don't know a perfect way, make sure to read the detailed process given below:
If your PC is accessible:
Step 1. Open Windows Start Menu. Then type Recovery and click on the "Recovery" option that appears under "Settings."
Step 2. Click on the "Open System Restore" link, and the restore window will open.
Step 3. Select either the most recent Restore point or pick one from the list. From here, follow the wizard to restore your PC.
If your PC doesn't boot:
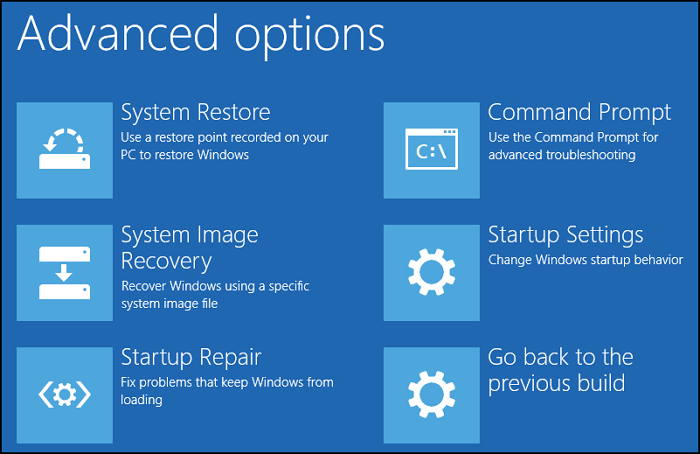
If your PC is not booting, you must go into Advanced Recovery using a bootable USB drive.
Step 1. Go to "Troubleshooting" > "Advanced Options" > "System Restore."
Step 2. Click on "System Restore," and it will open the Restore wizard, asking to select the date.
Step 3. Select the date you think the PC was in a good state, and follow the wizard to restore the PC.
The Epilogue
So, Guys! Hopefully, you have perfect knowledge of what a restore point in Windows is and how to use it. If you have some pending queries, you can ask them in the comment section below.
FAQs about Restore Point
Here are some of the most asked FAQs to help you resolve your pending queries efficiently.
1. Does restore point delete files?
No, the restore point doesn't delete the associated files. It backs up all the files on the system drive, including the user files.
2. How do I use a Microsoft Restore Point?
Go to "Control Panel". Then type Recovery. Select "Recovery" and open "System Restore." Select "Next" > "Restore Point" and then select Scan.
3. Does the System Restore Remove Viruses?
No. System restores don't remove any viruses from the files. However, if you restore your PC using Advanced Recovery, then the PC will be restored to a date when the virus was not there. So indirectly, it can remove the virus.
Was This Page Helpful?
Daisy is the Senior editor of the writing team for EaseUS. She has been working at EaseUS for over ten years, starting as a technical writer and moving on to being a team leader of the content group. As a professional author for over ten years, she writes a lot to help people overcome their tech troubles.
Related Articles
-
What Is macOS Catalina | Upgrade macOS Catalina Guide
 Brithny/2024-01-11
Brithny/2024-01-11 -
Turn On Secure Boot for Windows 11 Installation
 Tracy King/2024-01-11
Tracy King/2024-01-11 -
Hot Backup vs Cold Backup: Definition, Pros & Cons
 Daisy/2024-01-11
Daisy/2024-01-11 -
An Error Occurred While Starting Roblox - Proven Fixes ✔️
 Sherly/2024-03-14
Sherly/2024-03-14
