Virtual memory is a key essential of computer memory management. So, what exactly is it?
Computers rely on many things to operate properly. In order to access data and make it available for the computer's user, it relies on many key components. One of them is virtual memory. This factor of any computer ensures smooth performance and handling of day-to-day operations.

However, understanding virtual memory is a whole another thing. Mainly because it's vastly different from physical memory inside our computers. So, what is virtual memory? How does it work, and why is it so important? Let's find out.
What Is Virtual Memory?
Virtual memory, sometimes known as virtual storage, is a memory management technique in computer devices. The purpose of this memory is to ensure taking enough chunks from physical storage and show the size of the physical/main memory, which is much larger than the actual one.
It's made possible through the operating systems and their techniques over the years. This allows the operating system to map certain virtual memory towards the main memory using a mix of software and hardware methods.
And yes, this is the same system/virtual memory many tech experts suggest you should change to speed up your computer. And, since the primary purpose of virtual memory is to make application programming easier, it hides the fragmentation of physical memory.
Here's an example in DXDIAG command in Run:
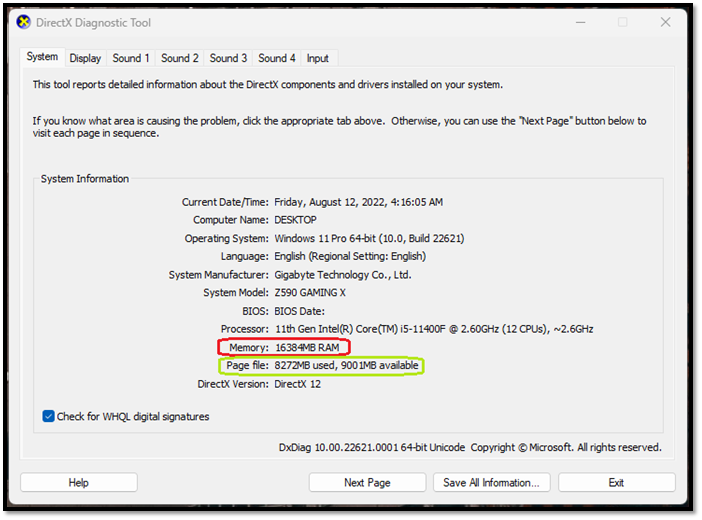
Marked in red is the system's physical memory, aka RAM. Whereas the numbers marked in green are the shared memory from our device to our Ram to ensure smooth operation. As for its usage, it's one of the essential parts of any computer operation/architecture.
In today's computers, this virtual memory is usually known as paged memory, which takes a chunk of our storage devices. Then, it allocates that storage to the physical memory in order for it to have an increased headroom.
While it doesn't directly work as an effective physical memory, it does assist in times of extreme loads and stress on the physical memory. And depending on the bus size of the Ram and the bus supported by the CPU, this can go up to twice the size of the actual memory.
For instance, if you have 8GB physical ram installed in a computer, then the paging file size might be a little over that, such as 8.5 GB. However, you can manually allocate more than that to ensure smooth operation.
But, it's important to remember that it takes that chunk out of your storage, effectively making it unavailable. That's one of the reasons some computers with smaller primary storage might suffer from slow operations or stutters.
Virtual Memory vs. Physical Memory
The difference between virtual memory and physical memory is literal. One is physical, other is virtual. However, to help you understand it, we must portray some key information. Here's a table for both:
| Virtual Memory | Physical Memory |
| Virtual memory is stored on a hard drive's allocated space to paging files | Physical memories are chips that you purchase and install in the DIMM slot on your motherboard |
| Virtual memory comes into play when physical memory or RAM is occupied | Physical memory or RAM is the primary memory employed by a computer from the get-go |
| Virtual memory is slower since it relies on hard disk drives or solid-state drives | Physical memory is meant to be fast and ensures higher-speed operations |
| Virtual memory can be increased in size manually by allocating more hard drive space | Physical memory is limited to the size of the chips present on a memory module |
| Virtual memory places information on the hard drive in the form of pages, hence the paging file size and name | Physical memory places data within the RAM chips and wipes them out once the operation is done, i.e., when you close a document |
| Adding more virtual memory won't make a visible difference | Adding more physical memory can visibly increase the performance of a computer |
These differences show that physical memory is faster and is meant for memory usage. However, virtual memory acts as a sort of backup when the physical memory is 100% in use. But, don't expect any miracles in performance by allocating more space to your virtual memory.
That brings us to a commonly asked question; is virtual memory better than RAM? The simple answer is no, it's not. But, one without the other is incomplete. You will always end up needing virtual memory for your physical memory to perform effectively.
How Much Virtual Memory Should You Set?
In today's common operating systems, such as Windows 10 and 11, the operating system automatically decides virtual memory or paging file size. However, if you feel like you need more, then here's what you need to remember:
- Minimum paging file size = 1.5 times the size of physical memory
- Maximum paging file size = 4 times the size of physical memory
So, here's a table to help you decide how much allocated disk space you should give to your virtual memory:
| Physical Memory Size | Minimum Paging File Size | Maximum Paging File Size |
| 8GB | 12GB | 32GB |
| 16GB | 24GB | 64GB |
| 32GB | 48GB | 128GB |
Now, it's easy to understand that not many people will have 32 gigs of Ram and 128GB of storage to spare. That's why it's best to leave it up to your operating system to decide how much paging file size is needed.
Simply because as you use your computer, the paging file increases with time. Because when you push your computer's memory to its limits, the operating system increases virtual memory size automatically.
How to Increase Virtual Memory on Windows 10?
While it's suggested that you allow Windows 10 or 11 to dynamically increase virtual memory, you can do so manually too. This is only recommended if you suffer from stutters or slow application performance. Therefore, here's what you can do:
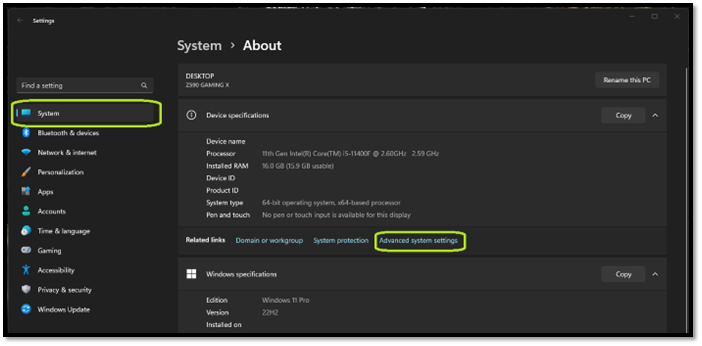
Step 1: Head to System settings
Step 2: Under Device specifications, find and click Advanced System Settings
Step 3: Click on Settings under the Performance banner
Step 4: Head to Advanced Tab, and click on Change under Virtual memory
Step 5: Uncheck "Automatically manage paging file size for all drives."
Step 6: Click the Custom size and set the Initial Size to 1.5x, and the Maximum to 4x the size of your RAM
Step 7: Click OK
That's how you can increase the virtual memory of your computer. Now, it's important to remember that users with 16GB ram or more do not have to manually increase their paging file size. Simply because operating systems will do it dynamically.
Bottom Line
We hope this article clears up any confusion and questions related to virtual memory. We also discussed the differences between virtual and physical memory, including how one is incomplete without the other.
Was This Page Helpful?
Daisy is the Senior editor of the writing team for EaseUS. She has been working at EaseUS for over ten years, starting as a technical writer and moving on to being a team leader of the content group. As a professional author for over ten years, she writes a lot to help people overcome their tech troubles.
Related Articles
-
Windows 11 Games Crash or Freeze? Don't Miss Quick Fixes Here!
 Tracy King/2024-04-07
Tracy King/2024-04-07 -
What Is Netstat Command and How to Use It
 Daisy/2024-01-11
Daisy/2024-01-11 -
Best External Hard Drive for PS3: Top 7 Picks for 2024
 Roxanne/2024-01-11
Roxanne/2024-01-11 -
What Is Windows Registry and How to Use It [Update 2024]
 Daisy/2024-01-11
Daisy/2024-01-11
