Most people use their computer without ever knowing how it works. They just open their web browser and start surfing the Internet. But there's a lot more to computers than that. In fact, there are all sorts of processes happening behind the scenes that you never see. One important process is direct memory access or DMA for short. Read on to learn everything you need to know about DMA and what it does for your computer.
What Is Direct Memory Access?
Direct memory access (DMA) is a process that allows specific hardware devices to access system memory independently of the CPU. This enables the device to perform tasks without interrupting the main processor, improving performance. DMA is used for devices such as disk controllers and network cards. You can also use it for data transfer between the memory and peripheral devices such as sound cards and graphics cards.
How Direct Memory Access Works?
DMA works by having a dedicated DMA controller that manages the data transfers between memory and the various devices that need to access it. The DMA controller will first need to be configured with the desired source and destination addresses, as well as the size of the data transfer. Once everything is configured, the DMA controller will initiate the transfer and monitor it until it is complete.
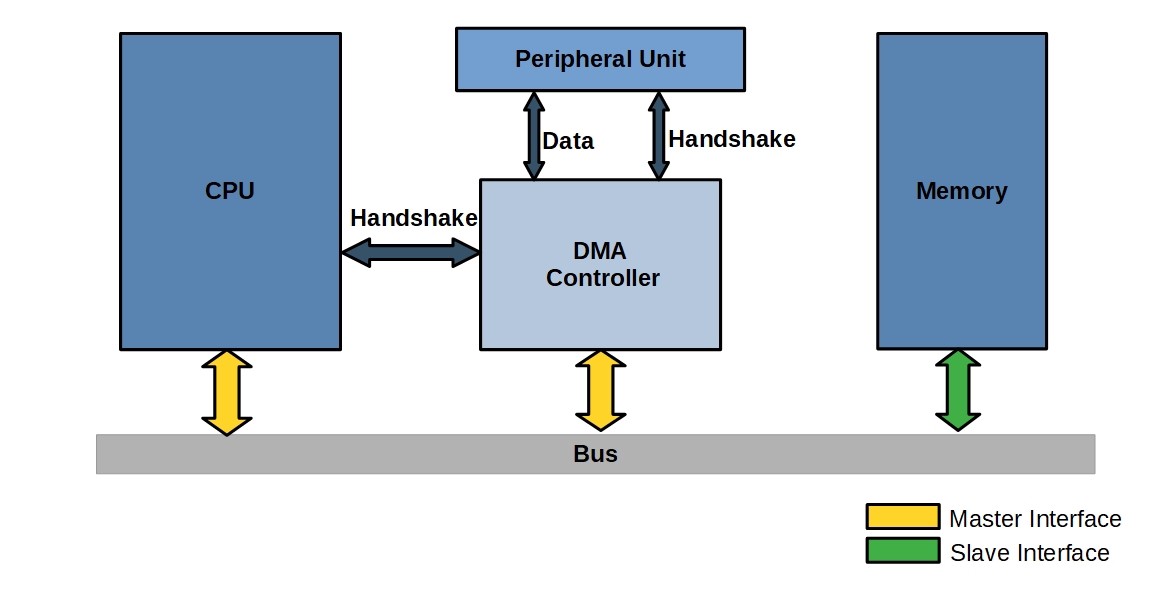
Since the DMA controller is handling the data transfer, the CPU is free to perform other tasks while the transfer is taking place. This can significantly improve the system's overall performance, as the CPU is not tied up with data transfer tasks.
There are some drawbacks to using DMA, however. First, it can be more difficult to debug issues when DMA is being used, as the CPU is not directly involved in the data transfer process. Secondly, DMA transfers can be slower than CPU-based transfers, as the DMA controller needs to access memory in a specific way. But, overall, DMA can be a valuable tool for speeding up data transfers and freeing up the CPU for other tasks.
Different Modes of Operation
DMA has three modes of operation: burst mode, cycle stealing mode, and transparent mode.
- Burst mode. In burst mode, the DMA controller takes control of the bus for a short time to perform a data transfer. The CPU can still access memory, but there may be a brief delay while the DMA controller finishes its task.
- Cycle stealing mode. In cycle stealing mode, the DMA controller takes control of the bus whenever the CPU is not using it. This can cause problems if the DMA controller needs to access memory while the CPU is also trying to use the bus.
- Transparent mode. In transparent mode, the DMA controller has full control of the bus and can access memory without involving the CPU. This is the most efficient way for the DMA controller to access memory, but it can cause problems if the CPU needs to access memory while the DMA controller is using the bus.
How to Enable Direct Memory Access?
DMA can be enabled in the BIOS or by using a software utility. To enable DMA in the BIOS, enter the BIOS setup utility and look for an option to enable or disable DMA. The exact location of this option varies depending on your motherboard and BIOS, but it is typically located in the "Advanced" or "Chipset" section. Once you have found the option, set it to "Enabled" and save your changes.
You can try using a software utility if you cannot find an option to enable DMA in the BIOS. Windows includes a utility called "Device Manager" that can be used to enable or disable DMA for devices. To access Device Manager, click Start, then type "device manager" into the search box. Device Manager will then show a list of all the devices installed on your computer. Find the device you want to enable DMA for and double-click it to open its properties. In the properties window, go to "Details" tab, then find the "DMA" setting and set it to "Enabled". Save your changes and close Device Manager.
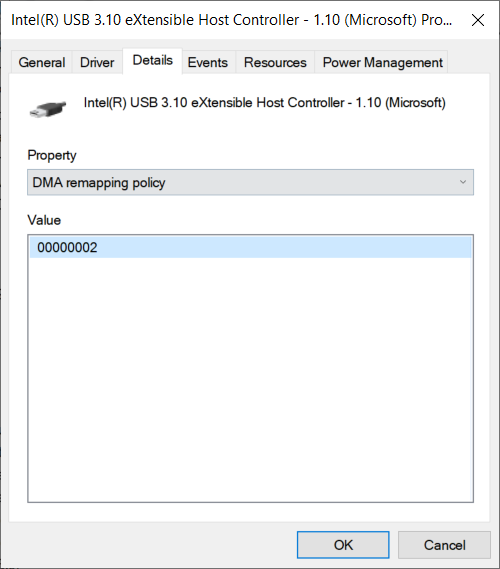
Enabling DMA may require a restart of your computer for the changes to take effect. Consult your motherboard or BIOS documentation for more information on enabling DMA.
Final words
Direct Memory Access is an important technology that can improve the performance of your computer. You can get the most out of your system by understanding how it works and enabling it.
Was This Page Helpful?
Daisy is the Senior editor of the writing team for EaseUS. She has been working at EaseUS for over ten years, starting as a technical writer and moving on to being a team leader of the content group. As a professional author for over ten years, she writes a lot to help people overcome their tech troubles.
Related Articles
-
Windows 11 24h2 Update: System/Hardware/CPU/LSTC Requirements
 Roxanne/2024-10-31
Roxanne/2024-10-31 -
What Is Minimum Processor State? Everything You Need to Know
 Daisy/2024-01-11
Daisy/2024-01-11 -
MSI File Extension - What Is .MSI? How to Open or Install It?
 Daisy/2024-01-11
Daisy/2024-01-11 -
Hot Corners Mac: How to Enable on macOS Sonoma/Ventura
 Brithny/2024-10-25
Brithny/2024-10-25
